Risk Management: A Core Driver of Financial Resilience for CFOs

Risk management is a structured process of spotting potential issues, monitoring risks, evaluating their impact, and implementing controls to protect the organization’s objectives. This involves the following key steps:
- Monitoring risks from sources such as market changes, operational failures, legal issues, or external events
- Evaluating their likelihood and potential impact
- Deciding on responses such as avoiding, mitigating, transferring, or accepting them.
Critically, risk management is no longer a one-time assessment. Continuous monitoring of internal and external risk signals ensures control remains effective, creating a living, adaptive cycle rather than a static compliance exercise.
For CFOs, risk management extends well beyond compliance, it is a core part of their job because risk management directly shapes financial performance, resilience, and the credibility of the finance function with boards, investors, and regulators. It enables informed decision-making, safeguards assets, and capitalizes on opportunities amid uncertainty. By adopting effective practices, organizations can preserve cash flow, ensure regulatory alignment, and strengthen stakeholder trust, transforming potential vulnerabilities into sources of competitive advantage.
Core Principles of Risk Management for CFOs
The pivotal roles CFOs play in risk management include identifying financial, operational, regulatory, cyber, and reputational risks that could hit the profit & loss or balance sheet and mitigating risks by leveraging financial data, scenario modeling, and predictive analytics to quantify exposures in monetary terms. Examples of risk mitigation include preventing potential revenue losses or increased borrowing costs.
Once identified, risks are prioritized based on severity, often using frameworks such as heat maps or value-at-risk (VaR) metrics tailored for executive review. Mitigation strategies follow, including avoidance such as exiting high-risk markets, reduction in investments related to insurance or hedging transfer or outsourcing, or acceptance with contingencies. Monitoring and reporting close the loop, with CFOs providing dashboards to the board that track key risk indicators (KRIs) such as liquidity ratios or debt covenants. This cyclical approach ensures adaptability, turning reactive firefighting into initiative-taking stewardship.
In an era of rapid disruptions caused due to pandemics, persistent inflation, high or volatile interest rates, currency volatility, trade wars, geo-political tensions, third-party risk, cyber and technology risk, and poor risk oversight has toppled big companies, while adept management has preserved billions.
The benefits of focusing on robust practices such as identifying real time risk visibility, scenario planning and stress testing, strong third party and liquidity monitoring, linking risk insights directly to financial impact can:
- Reduce earnings volatility by 20-30%,
- Prevent bad debt write offs,
- Stabilize cash flow, and
- Enhance credit ratings, lowering interest expenses.
CFOs who embed risk into strategic planning position their firms as resilient leaders, attracting talent and capital in competitive markets.
Use CFO.University’s Risk Management Assessment to benchmark where you staff, executives and Board of Directors stand on this key business topic.
Strengthening Risk Visibility Through Continuous Alert Monitoring:
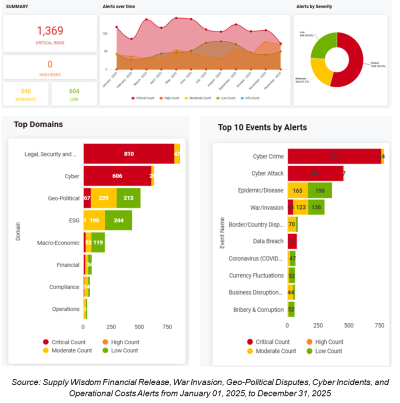
Over the past year, continuous monitoring risk intelligence alerts across key risk domains including financial performance, operational disruptions, cyber incidents, macro-economic developments, and geopolitical events has enabled timely identification of emerging threats. This ongoing visibility has supported proactive risk assessment, helped anticipate potential impacts on suppliers and operations, and strengthened overall decision-making and resilience.
Evolving CFO Role in Risk Oversight
Historically, CFOs focused on financial reporting and budgeting, but today’s role demands enterprise-wide risk leadership. Regulatory pressures such as Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), Dodd-Frank, or ESG disclosures mandate, CFO certification of internal controls, exposing them personally to penalties for lapses. Beyond compliance, CFOs now collaborate with CEOs on risk appetites, aligning them with corporate strategy e.g., tolerating innovation risks for growth but capping supply chain exposures.
Key Risk Responsibilities of the CFO:
- Fostering a risk-aware culture through training, integrating risk into Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for real-time visibility, and conducting stress tests that simulate recessions or cyber incidents.
- CFOs also champion technology adoption, such as AI-driven anomaly detection, to preempt fraud or forecasting errors. This evolution elevates the CFO from number-cruncher to strategic guardian, with boards increasingly trying compensation to risk-adjusted performance metrics like economic value added (EVA).
- Building cross‑functional risk forums with operations, IT, HR, and commercial teams so that finance has line‑of‑sight on non‑financial risks with financial implications.
Supply Chain Risks: A CFO’s Perspective
Supply chain risks are events or conditions that disrupt the flow of goods, services, information, or cash across your value chain, and they increasingly show up as missed revenue, margin erosion, and reputational damage on the CFO’s scorecard. In a globally connected environment, small disruptions at a single supplier or logistics node can cascade into significant financial and strategic impacts for the enterprise.
Supply chain risks have surged in prominence, amplified by globalization and events such as the COVID-19 lockdowns, Red Sea disruptions or tariff wars. These can cause delays, cost spikes, or shortages, directly compressing margins e.g., a 10% input price hike might wipe out quarterly profits for manufacturers.
The charts below illustrate the distribution of actual risk monitoring alerts by disruption type and severity of low, moderate, high, and critical alerts across key countries and organizations. This analysis helps identify recurring disruption themes, severity trends, and risk concentration, enabling leadership to focus on areas with elevated exposure and potential business impact.
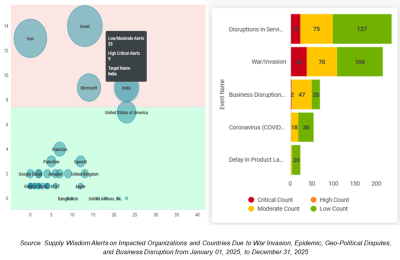
CFOs mitigate by conducting supplier audits and diversification analyses, mapping tier-1 through tier-3 dependencies to reveal single points of failure. Strategies include building strategic stockpiles, dual-sourcing critical components, and negotiating force majeure clauses with price adjustment mechanisms. Financial tools such as futures contracts hedge commodity volatility, while dynamic discounting improves supplier liquidity to ensure reliability.
A compelling example is the 2021 semiconductor shortage, which cost the auto industry US$210 billion. Firms such as Toyota, with CFO-led multi-region sourcing and inventory buffers, recovered faster than rivals, maintaining 5-7% higher EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) than competitors.
Counterparty Risks: Safeguarding Financial Relationships
Counterparty risks involve the potential default risk of business partners, suppliers, customers, banks, or derivatives traders threatening liquidity or triggering chain reactions. In credit crunches, unpaid receivables can strain cash reserves, while lender failures amplify borrowing costs.
CFOs counter this through rigorous due diligence: credit scoring models, financial statement reviews, and ongoing monitoring risk frameworks via risk monitoring product like the one offered by Supply Wisdom.
The 2008 crisis illustrates the stakes: Lehman Brothers’ collapse exposed counterparties to US$600 B in claims, bankrupting firms like MF Global. Post-crisis, CFOs at survivors like JPMorgan implemented central clearing and real-time exposure dashboards, slashing default-related losses. Today, with rising insolvencies amid high interest rates, CFOs stress-test portfolios quarterly to forecast cascading failures and adjust terms proactively.
Learn more on this risk here: Counterparty Risk Management: What Every CFO Needs to Know
Integrating Risks into CFO Decision-Making
Risk management must be embedded into every aspect of CFO decision-making.
- Planning and Forecasting: Integrating downside and upside scenarios into budgets and rolling forecasts, and linking each scenario to concrete actions such as cost measures, capex deferral, funding options
- Capital Allocation: CFOs must weigh risk-adjusted returns when approving investments. For example, entering a new market may promise growth but expose the firm to regulatory or currency risks.
- Liquidity Management: Maintaining adequate liquidity is a cornerstone of resilience. CFOs should stress-test cash flow under different scenarios, ensuring the company can withstand shocks.
- Technology and Data: Advanced analytics and AI-driven risk models enable CFOs to predict and monitor risks more effectively. However, CFOs must balance innovation with simplicity, ensuring tools are actionable rather than overly technical.
- ESG and Reputation: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) risks are increasingly material. CFOs must ensure compliance with ESG reporting standards and anticipate reputational risks tied to sustainability.
Practical Steps for CFOs to Take When Improving Risk Systems
CFOs should:
- Assemble cross-functional risk committees meeting quarterly.
- Invest in user-friendly dashboards visualizing KRIs against thresholds.
- Conduct annual enterprise-wide risk assessments with external validation.
- Simulate crises via tabletop exercises to evaluate response plans.
- Benchmark against peers using metrics like risk-adjusted return on capital (RAROC).
These steps not only avert crises, they accelerate agility. Firms with mature programs report 15% higher shareholder returns.
Long-Term Implications for CFO Leadership
Ultimately, risk management redefines CFO success from short-term metrics to sustained value creation. In boardrooms, CFOs articulate how mitigated risks underpin growth trajectories, justifying investments in resilience amid activist pressures. As climate and geopolitical risks intensify, CFOs who master this domain will lead transformations, securing legacies as indispensable strategists.
Strong risk practices lower the cost of capital by 50-100 basis points, boost operational efficiency, and foster innovation by providing a safety net. For CFOs, it is the difference between surviving turbulence and thriving through it.
Conclusion: Risk as a Strategic Enabler
When CFOs treat risk management as a strategic enabler rather than a compliance burden, they help create organizations that are not only financially sound, but also more agile, credible, and positioned for sustainable growth.
For CFOs, mastering supply chain risks transforms a potential vulnerability into a strategic advantage that safeguards earnings, optimizes capital, and builds investor confidence. By embedding risk-aware practices into forecasting, supplier oversight, and investment decisions, CFOs ensure their organizations remain agile amid disruptions like tariffs, geopolitical shifts, or climate events. Third-party risk monitoring supports CFO-led risk management by providing continuous, external risk intelligence across supply chains, third parties, locations, and events that can materially impact financial performance. By monitoring signals such as geopolitical developments, regulatory changes, cyber incidents, ESG issues, labor disruptions, and supplier distress, finance leaders gain early visibility into risks before they translate into revenue loss, margin pressure, or liquidity stress. This intelligence enables CFOs to link non-financial risk signals directly to financial exposure, strengthen scenario planning, and embed risk awareness into forecasting, capital allocation, and board reporting.
For more on the CFO and Risk Management dig into our two part series, Risk Management for CFOs
Identify your path to CFO success by taking our CFO Readiness Assessmentᵀᴹ.
Become a Member today and get 30% off on-demand courses and tools!
For the most up to date and relevant accounting, finance, treasury and leadership headlines all in one place subscribe to The Balanced Digest.
Follow us on Linkedin!
